ACEP Public Telemetry
Enjoy watching live events as they unfold, via the basic telemetry feed.
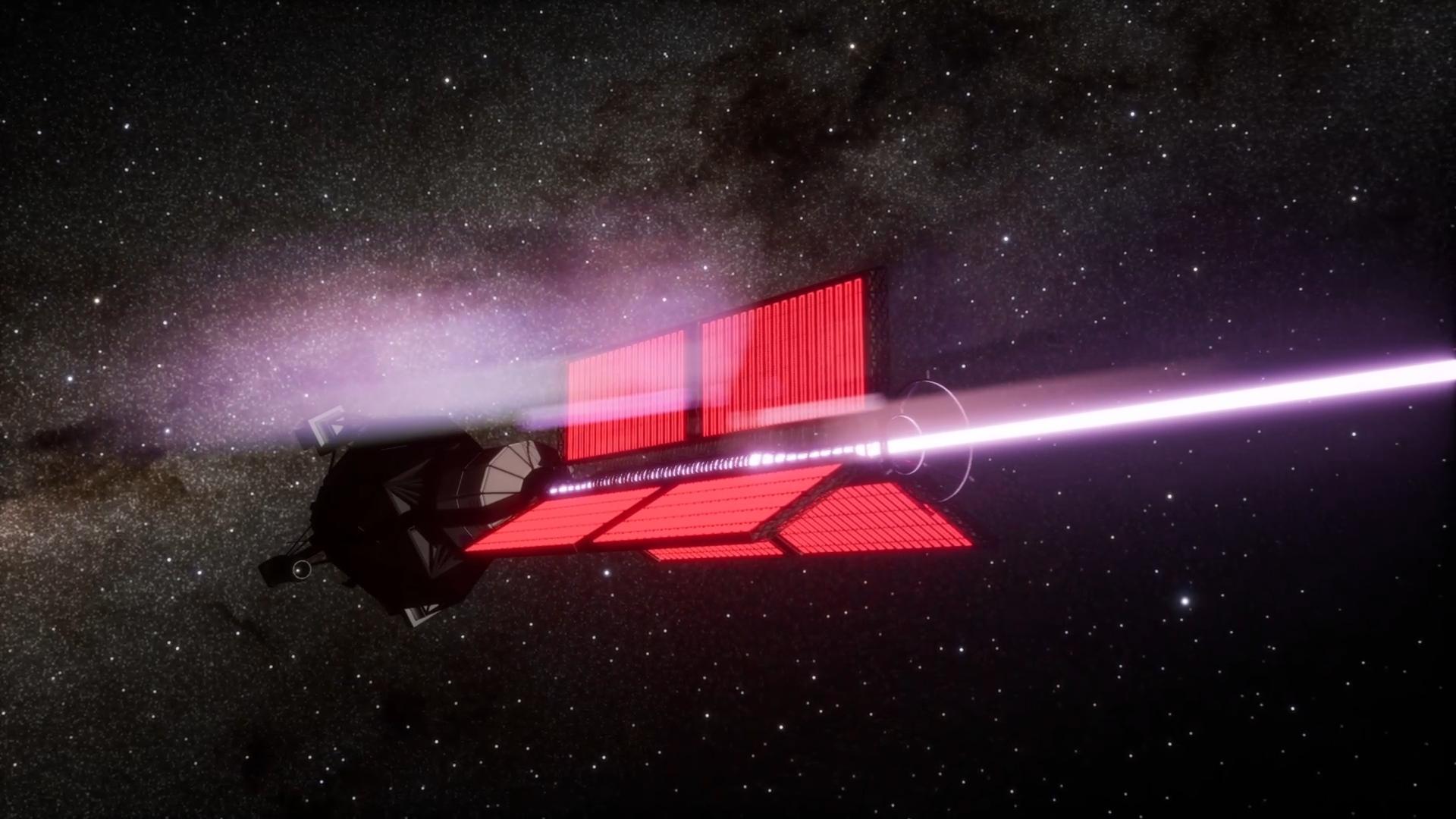
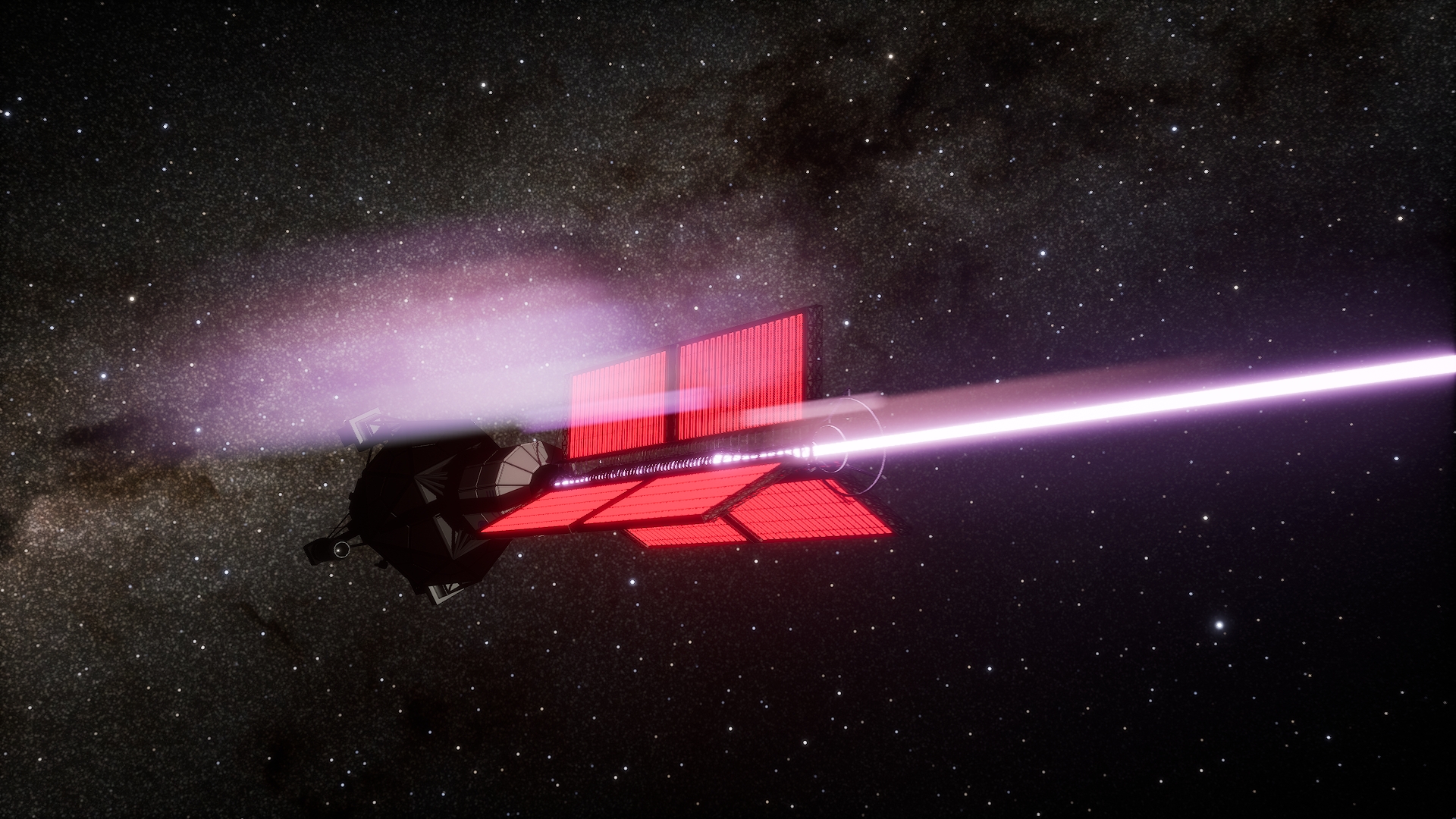
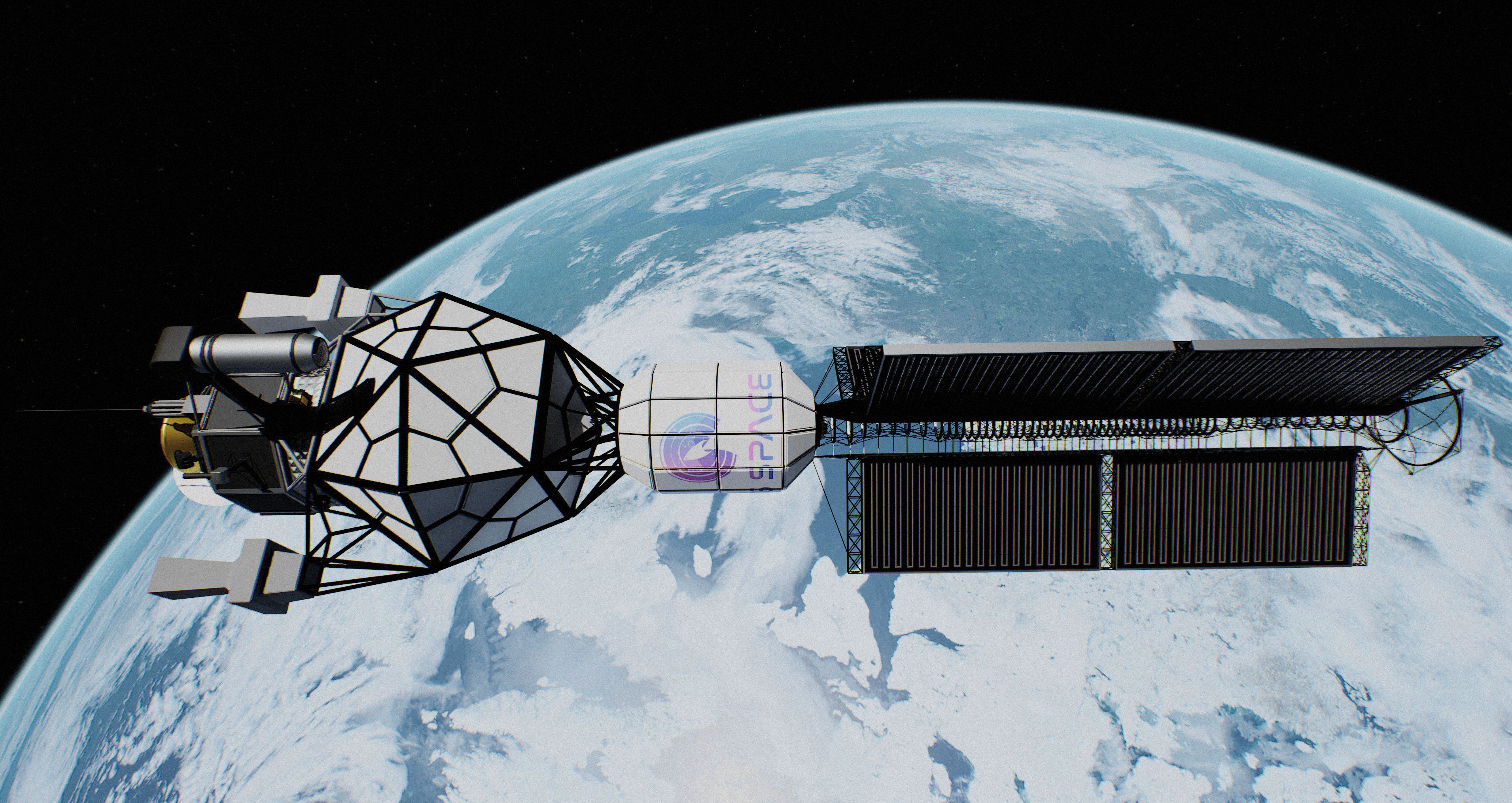
View ACEP Public TelemetryACEP is an uncrewed exploratory probe deployed as the first operational element of the 1gSpace program. Alongside autonomous reconnaissance of Proxima b, it functions as a long-duration technology demonstrator, establishing flight reliability, autonomous system behavior, and performance limits across multiple mission phases under interstellar conditions. Data derived from nominal and non-nominal operation is used to refine the design assumptions and constraints of subsequent crewed and logistical vehicles.
Enjoy watching live events as they unfold, via the basic telemetry feed.
View ACEP Public TelemetryFull-depth insight into the spacecraft's internal subsystems and state.
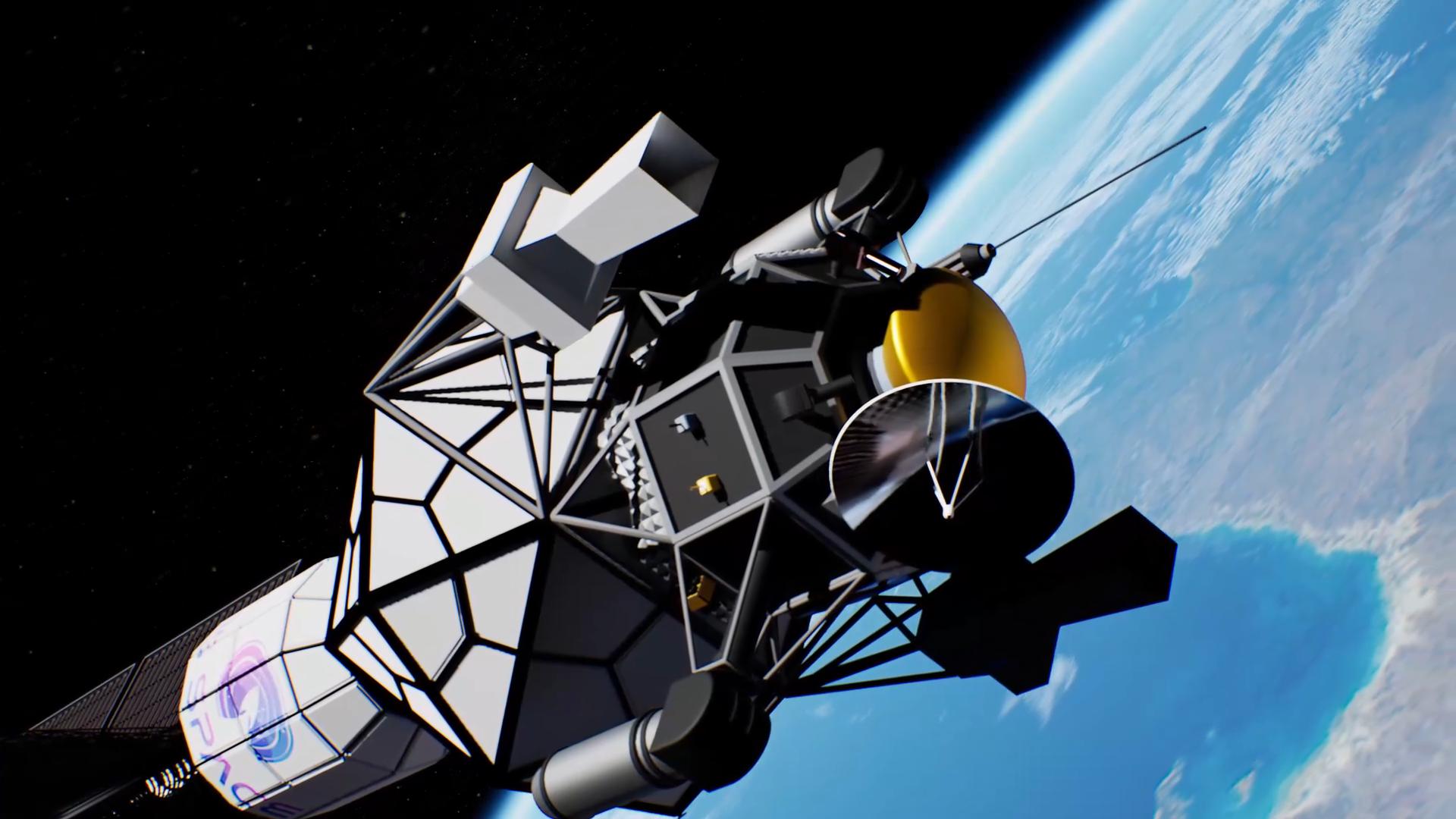
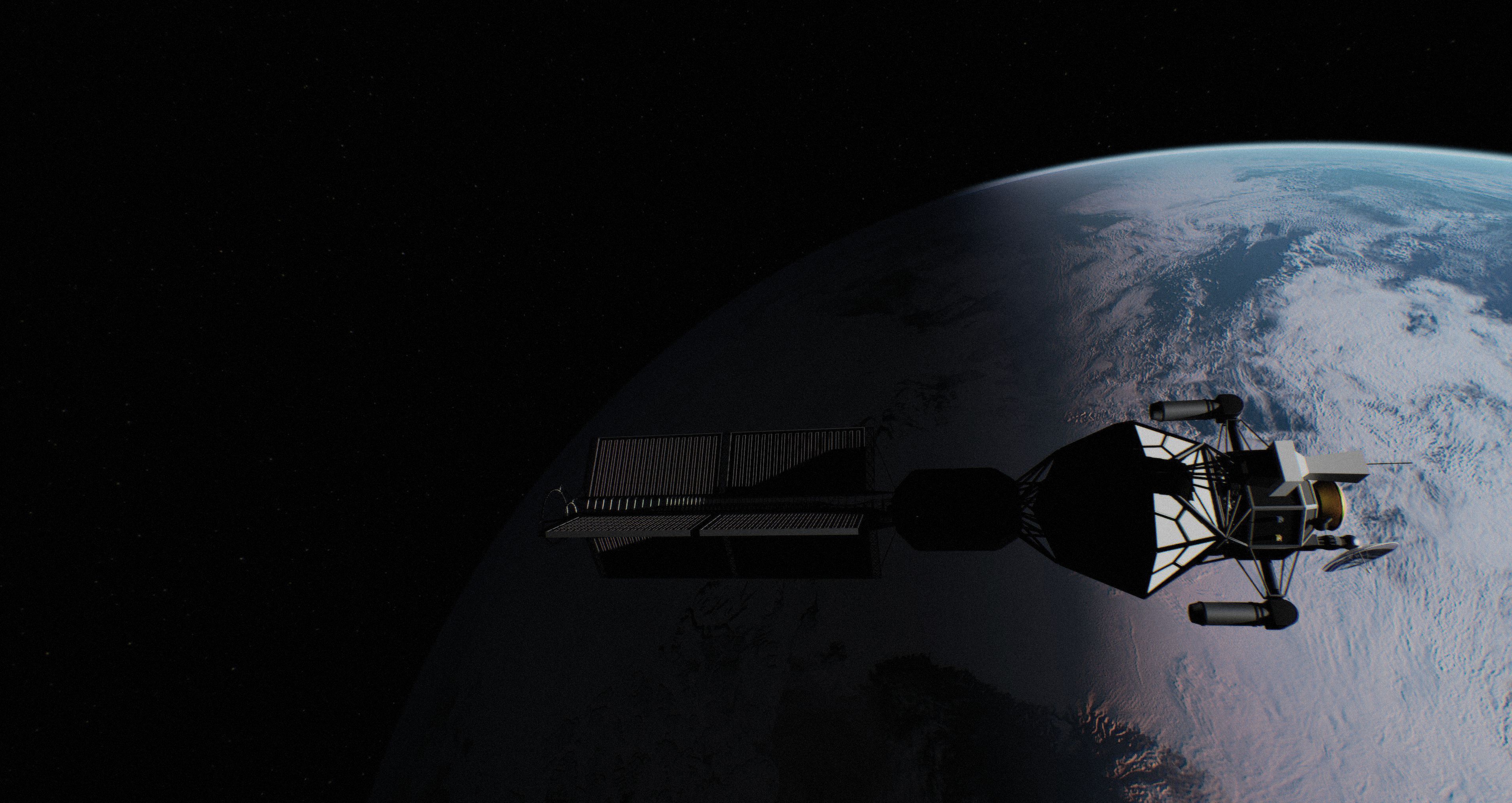
View ACEP Premium AccessThe Alpha Centauri Exploratory Probe (ACEP) is an autonomous deep-space spacecraft tasked with establishing a long-duration operational and observational presence at Proxima b. Its primary function is to characterize local environmental conditions, orbital dynamics, and surface and atmospheric context relevant to future sustained operations, while operating independently under interstellar communication delays.
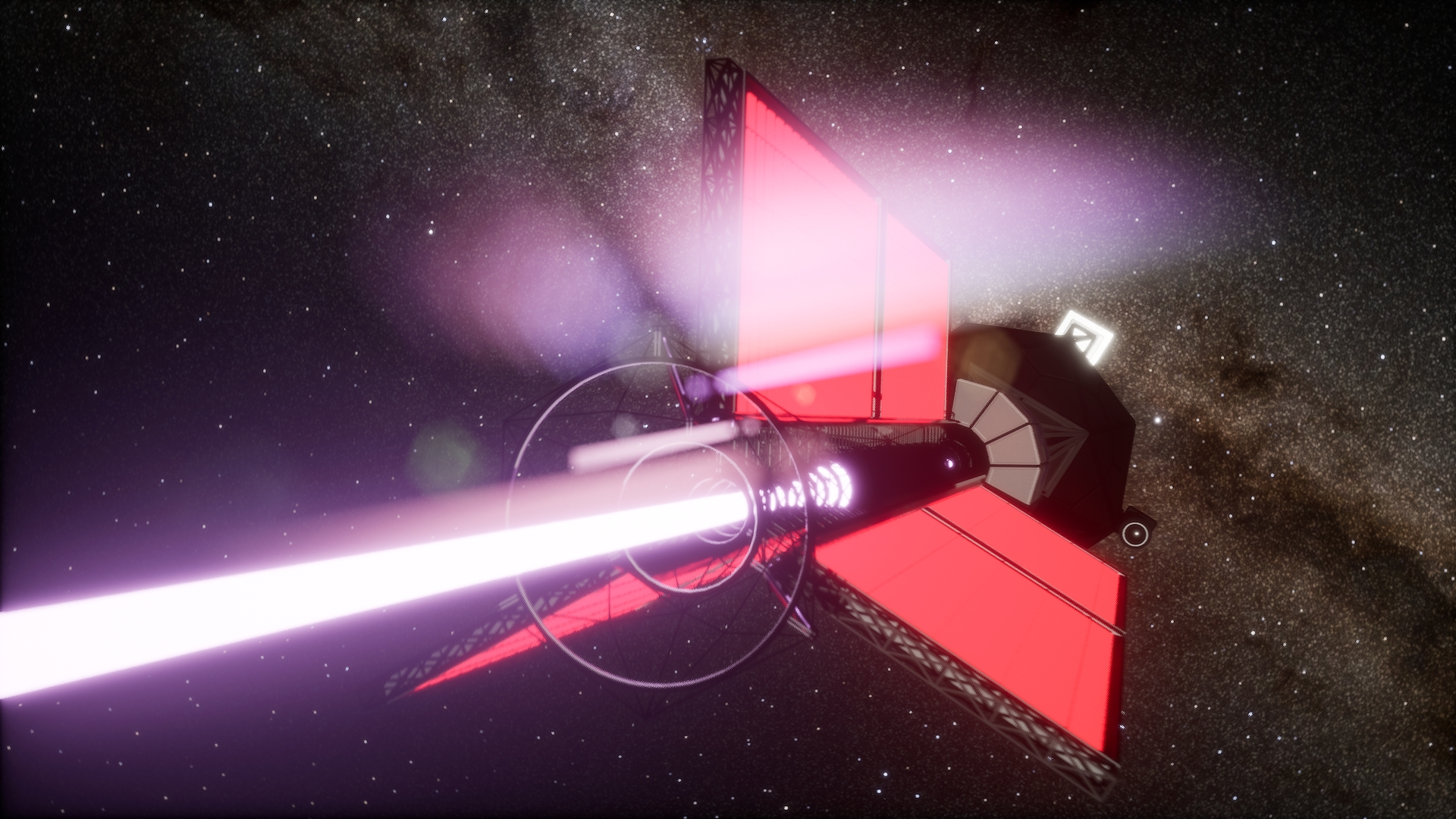
ACEP operates as both an exploratory mission and a long-horizon validation platform. Propulsion, power generation, and onboard systems are managed autonomously throughout all mission phases, allowing continuous thrust operations, adaptive power scheduling, and fault management without real-time ground intervention.
Scientific instrumentation supports remote and in situ observation across multiple mission phases. In addition to orbital sensing, the dedicated ACEP Atmos descent element performs a controlled atmospheric entry sequence, transmitting in situ pressure, temperature, and composition profiles to the orbiter prior to terminal descent.
Click on each category to view completed milestones.
Speed 0 equals LEO velocity at 200 km altitude